A Deep Dive into the Types of Projection in Geometric Design
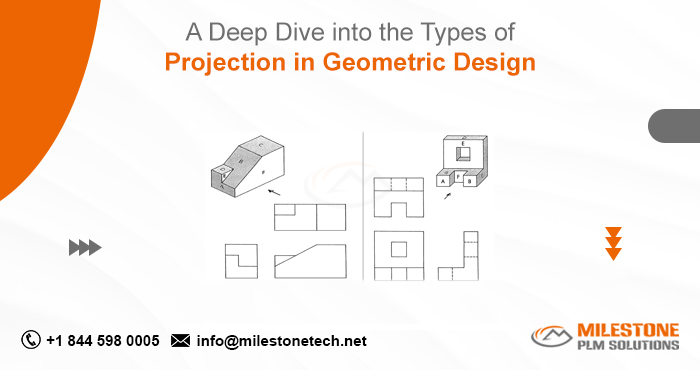
In the field of geometric design, projection is a fundamental technique that bridges the gap between three-dimensional objects and two-dimensional representations. From architectural blueprints to engineering drafts, projections play a pivotal role in accurately conveying the dimensions, angles, and spatial relationships of complex geometries. Understanding the various types of projection in geometric design is essential for professionals working in fields such as construction, manufacturing, architecture, and engineering.
What is Projection in Geometric Design?
Before diving into the different types, it’s essential to grasp the concept of projection in geometric design. Projection refers to the process of transforming a three-dimensional object into a two-dimensional representation by “projecting” points from the 3D object onto a plane (usually referred to as the projection plane). This transformation is vital in technical drawing, computer-aided design (CAD), and other applications requiring the visualization of three-dimensional objects on a flat surface.
Types of Projection in Geometric Design
There are two main categories of projection in geometric design: parallel projection and perspective projection. These two categories can be further subdivided into several types, each with its distinct characteristics and applications.
Parallel Projection
In parallel projection, the lines of sight, or projectors, are parallel to each other. This type of projection does not account for depth or distance, meaning that the size and shape of objects remain consistent, regardless of their position relative to the viewer. Parallel projections are primarily used in engineering and architectural design due to their accuracy and precision. There are two major types of parallel projection:
Orthographic Projection
Orthographic projection is the most common type of parallel projection used in engineering and technical drawings. It involves projecting the 3D object onto a plane using perpendicular lines to the plane. Typically, this technique is used to create multiple views of an object, including top, front, and side views, which are essential for interpreting complex structures.
- Advantages: Orthographic projections are highly accurate and ideal for technical drawings where measurements need to be precise. Since there is no distortion, it’s perfect for engineering blueprints and CAD models.
- Applications: Commonly used in mechanical engineering, construction, architecture, and manufacturing designs, orthographic projection allows engineers to fully define an object from different views without visual distortions.
Axonometric Projection
Axonometric projection is a type of orthographic projection that displays an object from multiple angles simultaneously. This is useful in cases where engineers need to visualize the entire object in a single view. There are three main types of axonometric projections:
- Isometric Projection: The most popular type, where the three axes of the object are equally inclined to the projection plane, creating an accurate yet visually intuitive representation. This projection is often used in CAD models, video games, and technical illustrations.
- Dimetric Projection: In this case, two of the object’s axes are equally inclined to the plane, while the third is different. It is used less frequently but is beneficial when two dimensions need more emphasis than the third.
- Trimetric Projection: Here, all three axes are inclined at different angles, making it the most complex type of axonometric projection. This type is rare but can be useful in specific engineering applications where three distinct dimensions need to be represented.
Oblique Projection
In oblique projection, the object is represented with one of its principal faces parallel to the projection plane, while the other faces are projected at an angle (usually 45 degrees) to the plane. This type of projection is less common in technical design but is often used in architectural drawings and diagrams where depth needs to be represented in a simple way.
- Advantages: It provides a quick way to sketch objects with depth, while maintaining accuracy in one plane.
- Applications: It is frequently used in simple architectural diagrams, illustrations, and early design phases when detail is less critical.
Perspective Projection
Unlike parallel projection, perspective projection mimics how the human eye sees the world. In this method, the lines of sight converge at a single point, known as the vanishing point. This technique introduces the concept of depth and distance, with objects appearing smaller as they move further away from the viewer. This makes perspective projection ideal for creating realistic representations of objects and spaces. The key types of perspective projection include:
One-Point Perspective
In one-point perspective, the projectors converge at a single vanishing point. This method is often used to represent objects that are directly facing the viewer, such as looking down a road or a hallway. One-point perspective is simple yet effective in conveying depth along a single axis.
- Applications: Used in architectural renderings, stage design, and interior spaces where a frontal view needs to demonstrate depth.
Two-Point Perspective
In two-point perspective, two vanishing points are used, usually positioned on the horizon line. This type of projection is useful for representing objects or spaces from an angled viewpoint, making it a popular choice in architecture and urban design.
- Applications: Architects and designers often use two-point perspective to represent buildings and urban layouts realistically.
Three-Point Perspective
Three-point perspective incorporates three vanishing points: two on the horizon and one either above or below the horizon. This technique provides a highly dynamic view, where objects are shown from an elevated or lowered viewpoint, making it ideal for dramatic architectural renderings or product designs.
- Applications: This projection is often used in product design, industrial design, and complex architectural renderings to depict objects or structures from exaggerated viewpoints.
Conclusion
Understanding the types of projection in geometric design is essential for anyone working in fields such as engineering, architecture, and manufacturing. Each type of projection has its own unique characteristics and applications, from the highly precise orthographic projection used in technical drawings to the realistic depth representation offered by perspective projection. Mastering these techniques allows professionals to communicate design ideas accurately and effectively, bridging the gap between conceptual designs and real-world applications.
As technology continues to advance, particularly in the realms of CAD and 3D modeling, the importance of selecting the appropriate projection method in geometric design becomes even more crucial for achieving accuracy, clarity, and precision in your work.
Follow Milestone PLM Solutions for Mechanical Industry Updates, CAD Tips and Global Mechanical News.
Milestone PLM Solutions with its exclusive delivery center in India is a global CAD, CAM & FEA services outsourcing partner serving the needs of the Mechanical, Millwork and Automotive industry since 2004. MILESTONE focuses on the unique needs of clients and believes in tackling real-life problems with efficiency, smooth and ease.
The MILESTONE team can assist you with Product Design, 3d Modeling, Drafting & detailing, Reverse Engineering, FEA Analysis and more. We support multiple software including AutoCAD, SolidWorks, Catia, NX, Inventor, Solidedge & Ansys etc. Our approach is to provide a dedicated team for each customer over ongoing project and deliver the quality output consistently.
With our state of art technology and large talent pool of Engineers, we are developing best in class solutions for our customers across the globe. We align with your culture and values to form unbreakable partnerships and are primed for success with over 100 employees and 150 customers in the US, Europe, India, and Asia.
You can email us at info@milestonetech.net and can log in to our website www. milestonetech.net to know more about our services and our work portfolio or contact us on +1-844-598-0005
