A Comprehensive Guide to Creating Assembly Drawings in Engineering
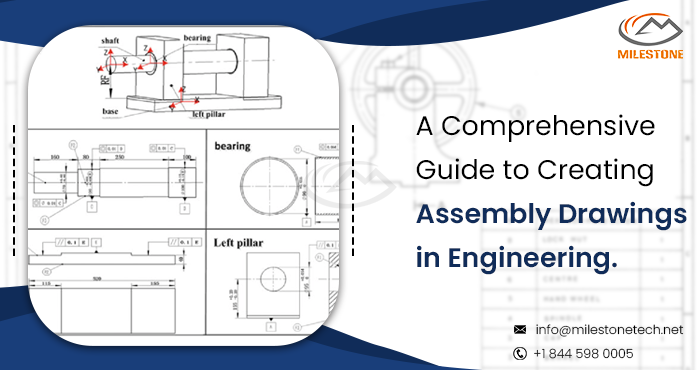
Assembly drawings play a crucial role in the field of engineering, serving as a bridge between design concepts and the physical realization of a product. These drawings provide a detailed representation of how various components come together to form a complete assembly, guiding manufacturers, engineers, and stakeholders through the production process. In this comprehensive guide, we will explore the key steps and best practices involved in creating effective assembly drawings in engineering.
1. Understanding the Purpose of Assembly Drawings:
Assembly drawings serve as a visual roadmap, showcasing the relationships and interactions between individual parts within a larger system. They communicate essential information such as part numbers, dimensions, materials, and tolerances. Engineers use assembly drawings to ensure that the manufactured product aligns precisely with the intended design, promoting consistency and accuracy in the production process.
2. Gather and Organize Design Data:
Before creating assembly drawings, it’s essential to gather all relevant design data, including 3D models, part specifications, and any assembly constraints. Ensure that all design data is accurate and up-to-date to avoid discrepancies during the manufacturing phase.
3. Choose the Right Software:
In today’s rapidly advancing technological landscape, engineering professionals have access to a plethora of software tools that facilitate the creation of assembly drawings. Selecting the right software is crucial for efficiency and accuracy. Some popular choices include AutoCAD, SolidWorks, and Revit. These tools provide a range of features, from 3D modeling capabilities to simulation and analysis, streamlining the assembly drawing process.
4. Create a Detailed Bill of Materials (BOM):
A Bill of Materials is a comprehensive list of all the components required to build the assembly. It includes part numbers, descriptions, quantities, and other relevant information. Creating a detailed BOM ensures that nothing is overlooked during the manufacturing process and helps in accurate procurement of materials.
5. Establish a Clear Hierarchy:
When creating assembly drawings, it’s important to establish a clear hierarchy that reflects the structure of the final product. Identify sub-assemblies and their relationships, allowing for a systematic approach to the manufacturing process. This hierarchy provides a logical flow to the assembly process, making it easier for both engineers and manufacturers to understand the overall structure.
6. Use Consistent Symbols and Annotations:
Consistency in symbols and annotations is key to creating assembly drawings that are easy to interpret. Standardized symbols and annotations improve communication and reduce the likelihood of errors during manufacturing. Ensure that the chosen symbols align with industry standards and are easily understood by all stakeholders involved in the production chain.
7. Incorporate GD&T (Geometric Dimensioning and Tolerancing):
Geometric Dimensioning and Tolerancing is a symbolic language used in engineering drawings to communicate design specifications. By incorporating GD&T into assembly drawings, engineers can convey information about the allowable variations in dimensions and geometric features. This ensures that the manufactured components meet the desired quality, standards and fits.
8.Review and Iterate:
Before finalizing assembly drawings, conduct thorough reviews with cross-functional teams, including design engineers, manufacturing experts, and quality control professionals. This collaborative approach helps identify potential issues early in the process, reducing the likelihood of costly revisions during production. Iterative reviews also contribute to continuous improvement in the design and manufacturing processes.
Types of Assembly Drawings
There are several types of assembly drawings, each serving a specific purpose and providing different levels of detail:
- Exploded Assembly Drawing: This type of drawing shows the components of an assembly separated from each other, highlighting their individual shapes and relationships with other components. Exploded drawings are particularly useful for visualizing complex assemblies.
- General Assembly Drawing: This type of drawing provides a complete overview of the assembly, showing all components in their assembled positions. General assembly drawings are commonly used for communicating the overall design and layout of the product.
- Installation Drawing: This type of drawing focuses on the installation of a specific component or assembly within a larger system. Installation drawings provide detailed instructions and diagrams for the installation process.
- Machine Shop Drawing: This type of drawing provides detailed information for machining individual components within an assembly. Machine shop drawings include dimensions, tolerances, and material specifications for each component.
- Schematic Assembly Drawing: This type of drawing uses simplified symbols and lines to represent the components and their connections in an electrical or hydraulic system. Schematic assembly drawings are used for understanding the functional relationships between components.
Conclusion:
Creating assembly drawings in engineering is a multifaceted process that requires attention to detail, precision, and collaboration. By following the steps outlined in this comprehensive guide, engineering professionals can produce accurate and effective assembly drawings that serve as a foundation for successful product realization. Embracing new technologies, By Using advanced CAD software, enhances the efficiency and accuracy of the entire process, aligning with the user’s interest in staying updated on technology in the field of engineering services.
Follow Milestone PLM Solutions for Mechanical Industry Updates, CAD Tips and Global Mechanical News.
Milestone PLM Solutions with its exclusive delivery center in India is a global CAD, Product Design partner serving the needs of the Mechanical Industry since 2004. MILESTONE focuses on the unique needs of clients and believe in tackling real-life problems with efficiency, smooth and ease.
We support multiple BIM software including SOLIDWORKS, AutoCAD, CATIA etc. Our approach is to provide a dedicated team for each customer over ongoing project and deliver the quality output consistently.
With our state of art technology and large talent pool of Engineers, we are developing best in class solutions for our customers across the globe. We align with your culture and values to form unbreakable partnerships and are primed for success with over 100 employees and 150 customers in the US, Europe, India, and Asia.
You can email us at info@milestonetech.net and can log in to our website www. milestonetech.net to know more about our services and our work portfolio or contact us on +1-844-598-0005
